When you think about Agile, you probably associate it with small teams of software developers. However, is it possible to enjoy the advantages of Agile software development in big companies?
Is it possible for a company with thousands of people and dozens of huge and complex projects to stay Agile? Let’s find out! Introducing a Scaled Agile Framework for enterprises.
Agile vs Big Enterprise
Although the challenges were similar for small and big companies, the size made a difference. Making quick decisions about goals and allocation of human resources, delegating the right tasks to the right people, and adapting to changes in a turbulent environment, is much more complex with multiple teams and projects onboard. There are also huge projects (counted in thousands of man-days) that simply cannot be delivered by a standard agile team (up to 8-10 people) in the required timeframe. During such assignments, an organization may also face difficulties with the identification and delivery of real value. It results in hassles with motivation, quality assurance, and a quick and apt response to customers’ needs. Is it even possible to address it following agile principles?
How To Scale Up Big Company and Stay Agile
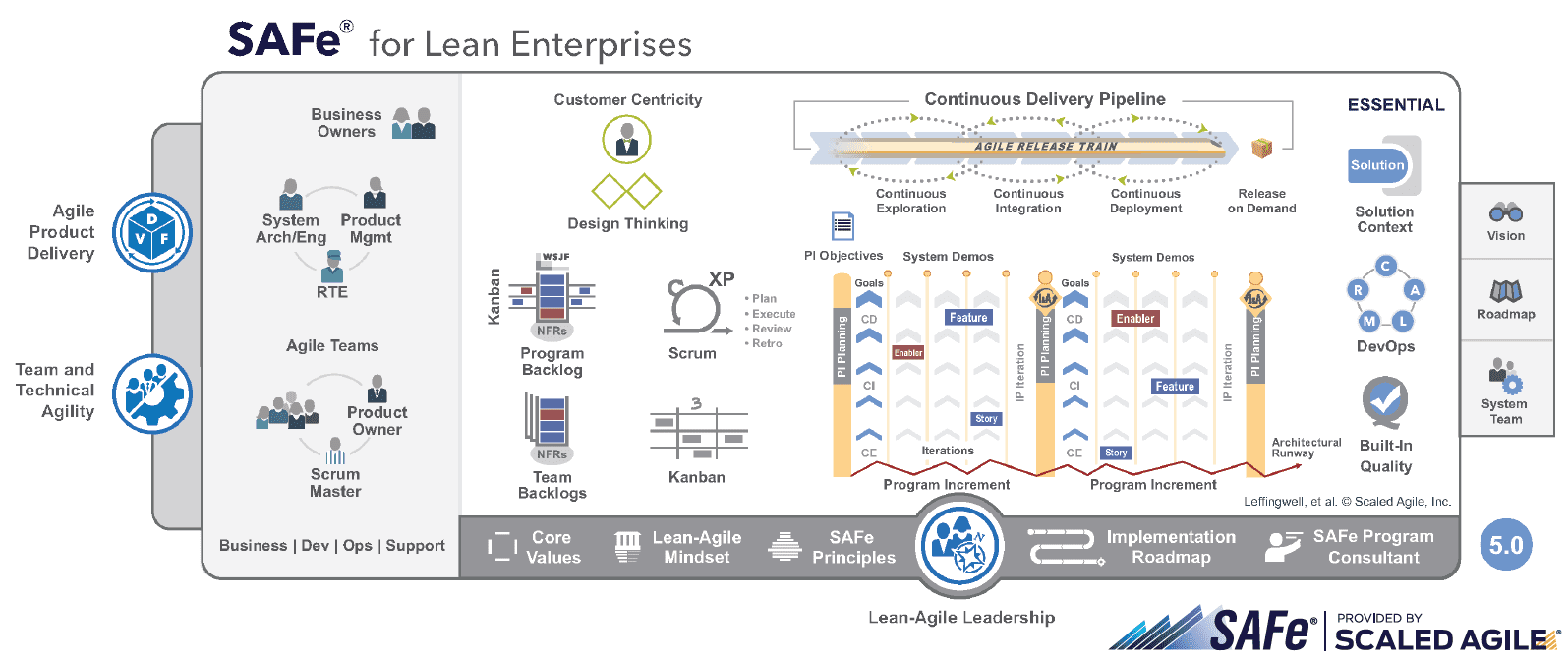
Fortunately, software development practitioners created an agile framework that tries to face these challenges. Scaled Agile Framework for Enterprise (SAFe) was first released in 2011. By 2020 version 5.0 has been presented. The framework is being developed and improved continuously.
SAFe makes use of several already existing concepts. Gathered and adjusted, they enhance the Agile scalability of an organization. The concepts are:
- Scrum
- Kanban
- Lean Production
- Lean UX
- Dev Ops
The collection of practices and principles taken from these concepts forms a framework that enables companies to scale-up while remaining agile. Transformed into a new quality, they result in a set of ten SAFe Lean-Agile principles that guide big organizations in their Agile path:
1. Take an economic view – first of all, everybody in the organization needs to understand their impact on the business value. They should also know the economic purpose of their project and the company as a whole. Architects, developers, testers, project managers, they all need to know the business justification of their involvement in the project.
2. Apply system thinking – connect with the first principle, everyone throughout the company needs to know his or her influence on the company. Seeing the big picture is crucial for motivation and efficient work.
3. Assume variability and preserve options – for as long as possible, you should assume that the business or economic environment will change. The Agile company should be ready for an abrupt shift. Therefore, it should maintain readiness for multiple solutions for a longer time instead of making all the decisions at the very beginning.
4. Build incrementally with fast, integrated learning cycles – every new iteration should bring new value to the customer. It not only satisfies the customer but also allows frequent feedback and steep learning curve.
5. Base milestones on objective evaluation of working systems – it’s crucial to base the project’s milestones on working functionalities. Vague success definitions lead to products that don’t deliver true value.
6. Visualize and limit WIP, reduce batch sizes, and manage queue lengths – it will help to increase throughput and stabilize the need for workforce. Smaller batches bring faster and predictable workflow. Queue lengths will influence wait times and improve cadence.
7. Apply cadence, synchronize with cross-domain planning – rhythmic delivery pattern synchronized across projects, and the company helps development teams focus on software development. Moreover, when the whole company works according to the same beat, it’s easier to integrate and coordinate various projects and deliverables.
8. Unlock the intrinsic motivation of knowledge workers – intrinsic motivation is an invaluable force that drives employees toward their goals. To make the most of it for your company, you should give them more autonomy, minimize limitations, and create a working environment where cooperation and common goals are supported.
9. Decentralize decision-making – few decisions influence business to such an extent that they need to reach top-tier management. Most decisions fall below this threshold. Top management benefits from more time for strategic thinking and employees get more independence.
10. Organize around value – gile is focused on delivering value. Such an approach changes the orientation of any organization. In fact, this is the core factor for a successful Agile organization.
Typical Benefits of Using SAFe for Enterprises
According to Scaled Agile, using SAFe results in productivity increased by 20 to 50 percent. But what’s the volume without quality? SAFe increases quality by defect reduction in the range of 25-75%. However, does it mean the development takes longer? Not at all. Time to market shortens by 30-75%. Last but not least, you can expect measurable increases in employee engagement and job satisfaction.
How Scaled Agile Framework for Enterprises Works in Practice?
To connect Agile and corporate needs, SAFe incorporates planning on several levels: Agile Teams, Programmes (Team of Agile Teams), Value Streams, and the Portfolio.
At the level of an Agile Team, SAFe is most similar to ‘traditional’ Agile. Small team creates value in 2-3 weeks Sprints.
On the level of Programmes, teams combine into Agile Release Trains. Teams within one train work according to cadence. As a result, they can work on several parts of one big product simultaneously.
Development teams within one or several Agile Release Trains work in coordination with specialists from other realms (e.g. marketing, quality assurance) to create a Value Stream. Value Stream is responsible for the creation of value from the moment when a customer’s need appears, way to the market release.
The highest level is a Portfolio gathering all the Value Streams running within the company. As you go from lower to higher levels of planning, the planning horizon gets longer.
How To Apply SAFe in Your Business?
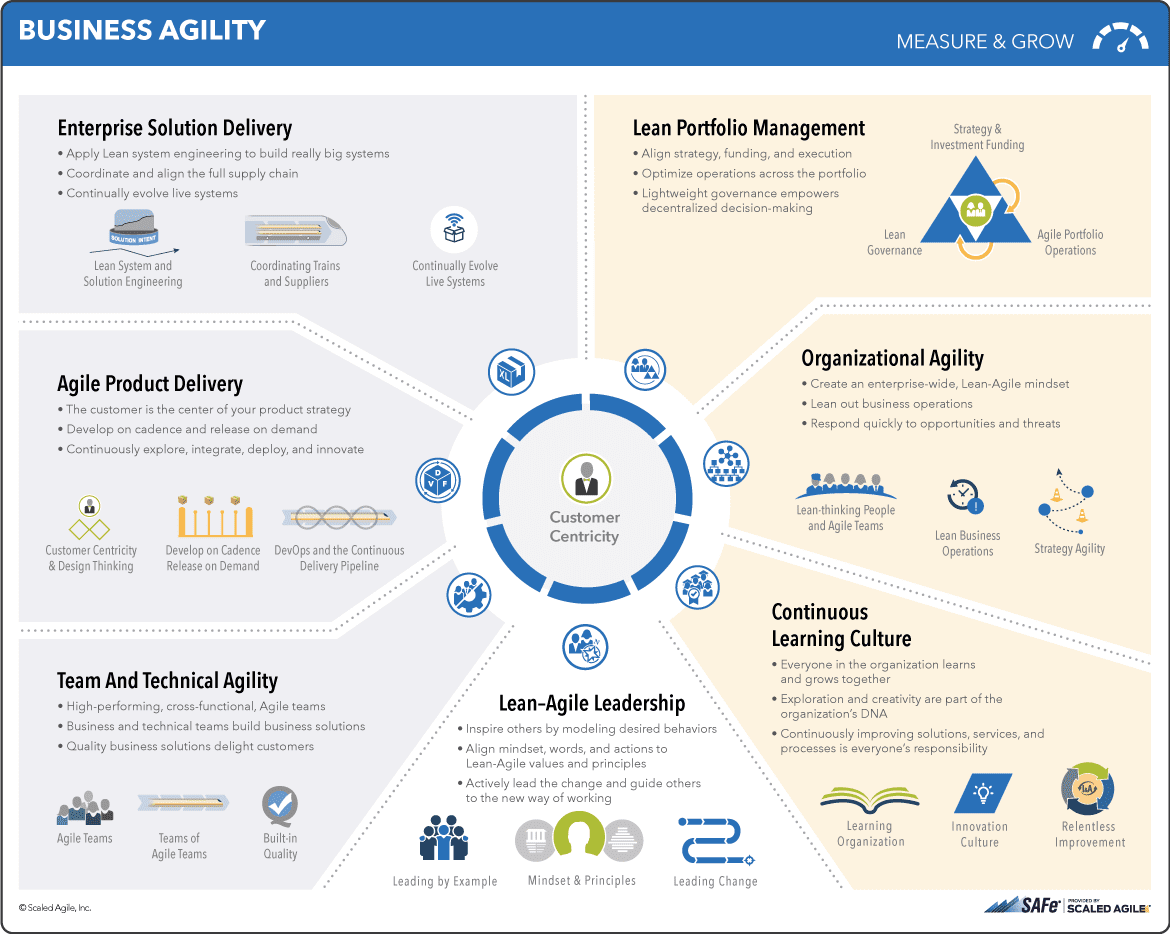
How to apply those SAFe principles in real life? There are 7 competencies an organization needs to develop on its way to agility. Every one of them brings the company one step closer. Together, they will lead to the creation of a competitive advantage and sustainable growth. The competencies include:
- Team and Technical agility
- Agile product delivery
- Enterprise solution delivery
- Lean portfolio management
- Organizational agility
- Continuous learning culture
- Lean-Agile leadership
Mastering any of these realms is a challenge. Scaling up big agile enterprise is even more difficult. It’s worth the effort though. Companies of this type will enjoy the advantages of both the Agile approach and the economies of scale available only for big players.
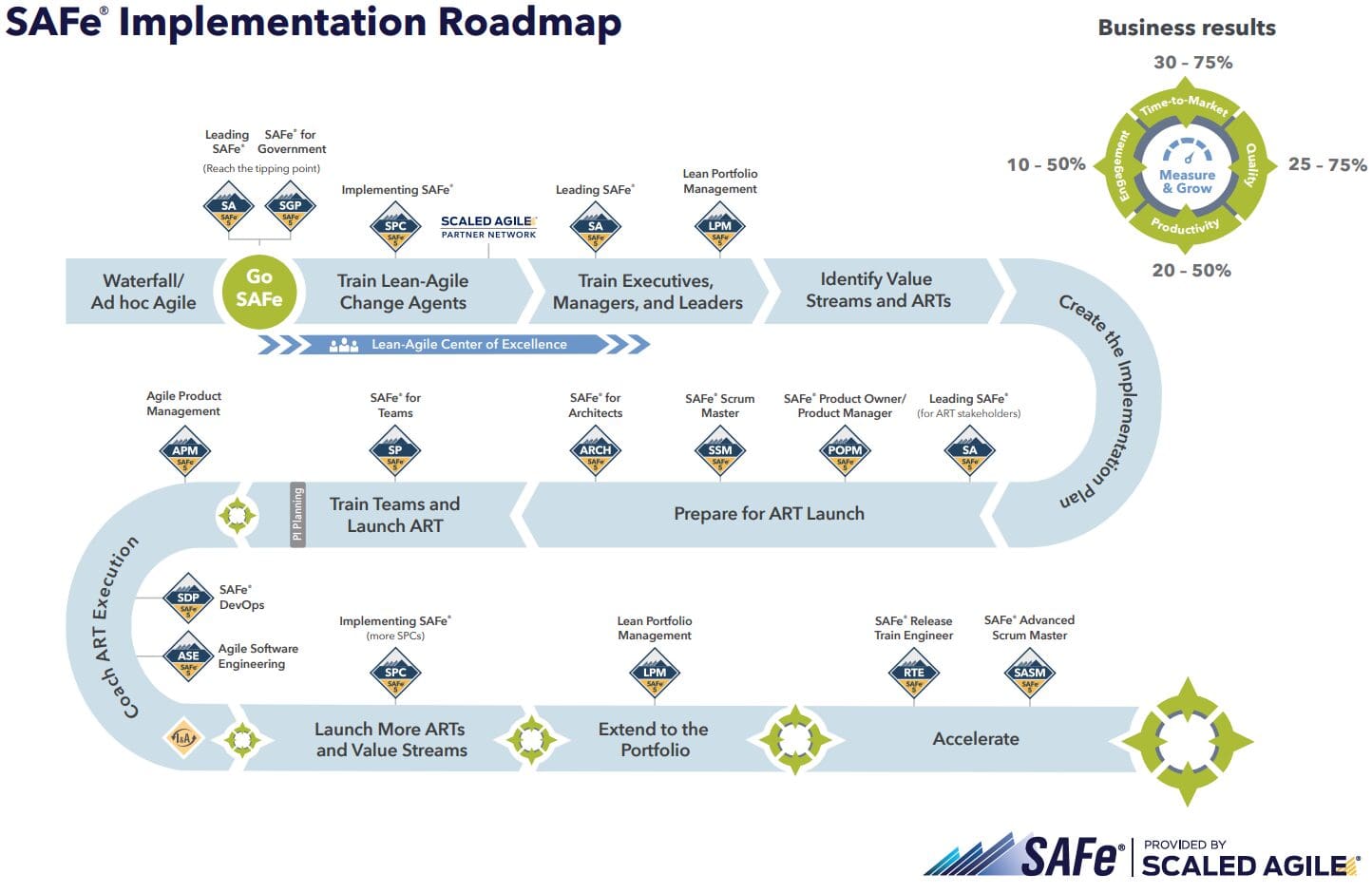
Agile Projects in Big Companies
As you see, big enterprises can benefit from Agile approach as well. Although as the company grows, its complexity grows as well, there’s always a space for agility. Unfortunately, there’s no off-the-shelf solution that fits each and every big company. Every enterprise faces its own challenges and needs to find its own way to tackle them. The key is to identify and use those elements of the SAFe framework that give the company the most value.
If you struggle on the way, please contact us for a totally free IT project consultation. According to your needs or problems you have faced, we’ll help with your transformation.
Read also: How Software Development Can Be Agile?
We will be glad to support you with incorporating Agile-Lean principles and helping you to earn higher profits.
Q: What is Scaled Agile Framework for Enterprises (SAFe)?
SAFe is an agile framework designed to help large organizations scale up while remaining agile in their software development process. It was first released in 2011 and is continuously being developed and improved.
Q: How does SAFe differ from traditional Agile?
SAFe is designed to address the specific challenges faced by large organizations, such as multiple teams and large and complex projects. It incorporates several existing concepts such as Scrum, Kanban, Lean Production, and DevOps to create a framework that allows for scalability while maintaining an agile approach.